Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yura, Kei; Go, Michiko*
no journal, ,
DNAs of Plant Organelles undergo RNA editing, a transcript repair mechanisms. Those RNA editing sites seems to be located uniformly on pre-mature mRNA. This previous finding suggested that RNA editing has nothing to do with protein function. In this study, we challenged this idea based on our new database gathering all the known RNA editing sites combined with protein three-dimensional structures. We gathered 1923 RNA editing sites out of 365 pre-mature mRNAs. We have investigated and found a good correlation between the site undergoing RNA editing and protein three-dimensional structure. The finding may suggest mechanisms and evolution of RNA editing.

Sato, Katsuya; Narumi, Issei; Oba, Hirofumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tamada, Taro; Arai, Shigeki; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Honjo, Eijiro; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Adachi, Motoyasu; Tamada, Taro; Sato, Katsuya; Yura, Kei; Narumi, Issei; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
PprA is cloned from the bacteria and the novel DNA repair protein that plays an important role in the resistance. This study is aimed to reveal the structure function relationship of PprA. The recombinant PprA protein was purified from E. coli. The interactions of PprA with DNA were analyzed by gel shift assay and gel filtration. The results showed that (1) at least 280 molecules of PprA can bound to a DNA molecule of pUC19 composed of 2686bp (2) the formation the complex of PprA and DNA depends on Mg, Ca and Sr ions at low concentration (3) the formation the complex of PprA and DNA depends on the concentration of the salt at the range of 0 to 0.4M sodium acetate. In addition, the result indicated that the complexes of PprA and DNA can form larger complex depending on the concentration of PprA molecule, when using linear double stranded DNA. This suggests that PprA may locate two terminals of a DNA molecule damaged by radiation at near distance for DNA repairing.

Sato, Katsuya; Oba, Hirofumi; Sghaier, H.*; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
In an effort to gain an insight into the role of LexA2 of  in the radiation response mechanism, gene disruptant strains were generated and investigated. The intracellular level of RecA increased in
in the radiation response mechanism, gene disruptant strains were generated and investigated. The intracellular level of RecA increased in 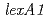 and
and 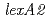 disruptant strains following irradiation as in the wild-type strain. These results indicated that the two LexA homologs did not possess functional overlap regarding the induction of RecA. The
disruptant strains following irradiation as in the wild-type strain. These results indicated that the two LexA homologs did not possess functional overlap regarding the induction of RecA. The 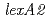 disruptant strains exhibited a much higher resistance to
disruptant strains exhibited a much higher resistance to  rays than the wild-type strain. Furthermore, a luciferase assay showed that
rays than the wild-type strain. Furthermore, a luciferase assay showed that  promoter activation was enhanced in the
promoter activation was enhanced in the 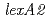 disruptant strain following
disruptant strain following  irradiation. The
irradiation. The  gene encoding the novel radiation-inducible protein PprA plays a critical role in the radioresistance of
gene encoding the novel radiation-inducible protein PprA plays a critical role in the radioresistance of  . The increase in radioresistance of the
. The increase in radioresistance of the 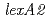 disruptant strain is explained in part by the enhancement of
disruptant strain is explained in part by the enhancement of  promoter activation.
promoter activation.
 1 chain and IL-4 receptor
1 chain and IL-4 receptor 
Honjo, Eijiro; Shoyama, Yoshinari; Tamada, Taro; Arima, Kazuhiko*; Kanaji, Sachiko*; Izuhara, Kenji*; Kuroki, Ryota
no journal, ,
The receptor binding to Interleukin (IL)-13 is composed of the IL-13 receptor  1 chain (IL-13R
1 chain (IL-13R 1) and the IL-4 receptor
1) and the IL-4 receptor  chain (IL-4R
chain (IL-4R ). In order to investigate the interaction of IL-13 with IL-13R
). In order to investigate the interaction of IL-13 with IL-13R 1 and IL-4R
1 and IL-4R , the DNA fragments coding the extracellular regions of human IL-13R
, the DNA fragments coding the extracellular regions of human IL-13R 1 and the IL-4R
1 and the IL-4R , containing a cytokine receptor homologous region, were fused with human Fc and expressed by silkworm-baculovirus system. Size exclusion chromatography did not reveal association between IL-13 and IL-13R
, containing a cytokine receptor homologous region, were fused with human Fc and expressed by silkworm-baculovirus system. Size exclusion chromatography did not reveal association between IL-13 and IL-13R 1 under these conditions, but the clear association of IL-13 and IL-13R
1 under these conditions, but the clear association of IL-13 and IL-13R 1 was observed after adding IL-4R
1 was observed after adding IL-4R . This indicates that both extracellular regions of IL-13R
. This indicates that both extracellular regions of IL-13R 1 and IL-4R
1 and IL-4R have functions, and the association between IL-13 and IL-4R
have functions, and the association between IL-13 and IL-4R increases the IL-13 affinity to IL-13R
increases the IL-13 affinity to IL-13R 1.
1.
Nakagawa, Mayu; Sakamoto, Ayako; Takahashi, Shinya*; Tanaka, Atsushi; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 and REV1 protein in Arabidopsis
and REV1 protein in ArabidopsisSakamoto, Ayako; Takahashi, Shinya*; Iwai, Shigenori*; Shimizu, Kikuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English